Improving Thoracic Mobility in Throwers
It goes without saying that all rotational sport athletes need adequate thoracic spine (upper body) mobility in order to create appropriate separation as they work to transfer force from the lower extremity to the upper extremity during swings, throws, shots, and changes of direction. In a throwing population, however, you need to take some special precautions as you work to build it.
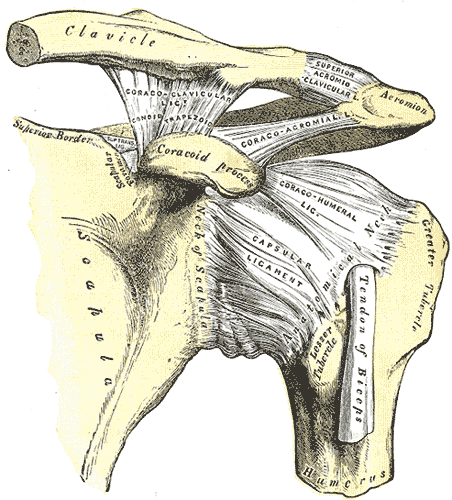
One thing we know about pitchers is that their shoulder external rotation improves over the course of a season, and this likely takes place because the ligamentous structures in the front of the shoulder become looser. In this image of a left shoulder, it would be the area labeled “capsular ligaments:”
Effectively, the looser one’s anterior capsule is, the more external rotation one will have. The problem, however, is that if this area becomes too loose, the biceps tendon must pick up the slack as an important anterior stabilizer during external rotation. Additionally, there are many nerve structures at the anterior shoulder that can be irritated because the humeral head isn’t controlled. This is yet another reason why it’s not a good idea to stretch a throwing shoulder into external rotation. In this video, I go into greater detail:
This knowledge gives rise to two thoughts:
1. If we lack thoracic rotation, our arm will drag during the pitching delivery, as it’s a means of creating better separation (albeit in the wrong places). Guys who have quick arms can often make up for it, but still inevitably irritate the anterior shoulder over time. So, if your thoracic rotation stinks, you’ll need to try to find more external rotation in the wrong places. Additionally, if we lack thoracic extension, we often substitute lumbar extension (lower back arching) to maintain an upright torso. These guys wind up with low back pain, oblique strains, and hip issues.
2. We can’t just throw any thoracic mobility drill at throwers, particularly in the early off-season, when the anterior shoulder is all stretched out and it may be the path of least resistance. As an example, the kettlebell arm bar might be a great drill for many folks in the population, but I would never use it with a thrower:
Instead, particularly in the early off-season, we need to pick drills that heavily emphasis thoracic movement independent of humeral (arm) movement. Here’s a progression we might use over the course of the off-season:
Off-Season Months 1-2 (and during the in-season phase): Supine Alternating Shoulder Flexion on Doubled Tennis Ball, Thoracic Extension on Roller, Rock-Back Quadruped Extension-Rotation
Off-Season Months 3-4: Side-Lying Windmill, Bent-Over T-Spine Rotation
You’ll notice that these options integrate a lot more humeral movement. In many cases, you can use them earlier in the off-season, but only if they’re coached really meticulously to ensure athletes are moving in the right places.
We use these exercises right after our foam rolling and positional breathing drills during the warm-up, and before anything we’d do to directly work on scapular stabilization and rotator cuff strength/timing. Hopefully, this article gives you a little feel for not just some of the exercises we may use, but also the way we’d program them throughout the competitive season.
If you’d like to learn more about how we manage throwers, be sure to register for one of our Elite Baseball Mentorships. The next one will take place June 14-16 in Hudson, MA.





