Getting Geeky with AC Joint Injuries
Getting Geeky with AC Joint Injuries
Lately, I’ve gotten quite a few in-person evaluations and emails relating to acromioclavicular (AC) joint issues. As such, I figured I’d devote a newsletter to talking about why these injuries are such a pain in the butt, what to do to train around them, and how to prevent them in the first place (or address the issue once it’s in place).
First off, there is a little bit about the joint that you ought to know. While the glenohumeral joint (ball-and-socket) is stabilized by a combination of ligamentous and muscular (rotator cuff) restraints, the AC joint doesn’t really have the benefit of muscles directly crossing the joint to stabilize it. As such, it has to rely on ligaments almost exclusively to prevent against “shifting.”

As you can imagine, then, a traumatic injury or a significant dysfunction that affects clavicle positioning can easily make that joint chronically hypermobile. This is why many significant traumatic injuries may require surgery. While almost all Grade 4-6 separations are treated surgically, Grades 1-2 separations are generally left alone to heal – with Grade 3 surgeries going in either direction.
In many cases, you’ll actually see a “piano key sign,” which occurs when the separation allows the clavicle to ride up higher relative to the acromion. Here’s one I saw last year that was completely asymptomatic after conservative treatment. It won’t win him any beauty contests, and it may become arthritic way down the road, but for now, it’s no problem.
Now that I’ve grossed you out, let’s talk about how an AC joint gets injured. First, we’ve got traumatic (contact) injuries, and we can also see it in people who bench like this:
Actually, that’s probably a fractured sternum, but you can probably get the takeaway point: don’t bounce the bar off your chest, you weenie. But I digress…
Insidious (gradual) onset injuries occur just as frequently, and even moreso in a lifting population. Most of the insidious onset AC joint problems I’ve encountered have been individuals with glaring scapular instability. With lower trapezius and serratus anterior weakness in combination with shortness of pec minor, the scapula anteriorly tilts and abducts (wings out) – and you’ll see that this leads to a more inferior (lower) resting posture.
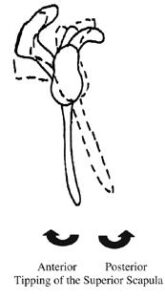
In the process, the interaction between the acromion (part of the scapula) and clavicle can go a little haywire. The acromion and clavicle can get pulled apart slightly, or the entire complex can get pulled downward a bit. In this latter situation, you can also see thoracic outlet syndrome (several important nerves track under the clavicle) and sternoclavicular joint issues in addition to the AC joint problems we’re discussing.
As such, regardless of whether we’re dealing with a chronic or insidious onset AC joint issue, it’s imperative to implement a good scapular stabilization program focusing on lower trapezius and serratus anterior to get the acromion “back in line” with the clavicle. Likewise, soft tissue and flexibility work for the pec minor can also help the cause tremendously.
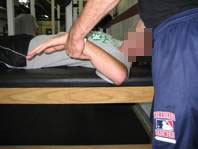
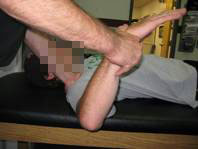
Anecdotally, a good chunk of the insidious onset AC joint problems I’ve seen have been individuals with significant glenohumeral internal rotation deficits (GIRD). The images below demonstrate a 34-degree GIRD on the right side.
It isn’t hard to understand why, either; if you lack internal rotation, you’ll substitute scapular anterior tilt and abduction as a compensation pattern – whether you’re lifting heavy stuff or just reaching for something. And, as I discussed in the paragraph above, a scapular dyskinesis can definitely have a negative effect on the AC joint.
Lastly, you can’t ever overlook the role of thoracic spine mobility. If your thoracic spine doesn’t move, you’ll get hypermobile at the scapulae as a compensation – and we already know that’s not good. And, as Bill Hartman discussed previously, simply mobilizing the thoracic spine can actually improve glenohumeral rotation range-of-motion, particularly in internal rotation. Inside-Out is a fantastic resource in this regard – and is on sale this week, conveniently!
So, as you can see, everything is interconnected! In part 2 of this series, I’ll discuss training modifications to work around acromioclavicular joint problems and progress back to more “normal” training programs.
New Blog Content
Birddogs, Continuing Education, and Terrible Journalism
Exercise of the Week: Dumbbell Reverse Lunge
All the Best,
EC
Sign-up Today for our FREE Baseball Newsletter and Receive a Copy of the Exact Stretches
used by Cressey Performance Pitchers after they Throw!